ISO Glossary and Iconography
Glossary of Terms
A
Administrator Access is defined as a level of access above that of a standard end-user. This definition is intentionally vague to allow the flexibility to accommodate varying systems and authentication mechanisms. Under most circumstances this level of access is relegated to privileged accounts. The following are examples of administrator access:
- In a traditional Microsoft Windows environment, members of the Power Users, Local Administrators, Domain Administrators and Enterprise Administrators groups would all be considered to have Administrator Access.
- In a traditional UNIX or Linux environment, users with root level access or the ability to sudo would be considered to have Administrator Access.
- In an application environment, users with elevated privileges, ‘super-user’, system or database administrator roles and responsibilities would be considered to have Administrator Access.
- Network and other infrastructure systems administrators are also considered to have Administrator Access.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments.
Authentication factors are categories of credentials used to verify a user's identity. These are commonly used in multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems to enhance security. Typically, these factors are grouped into three types:
- Something you know – e.g. a PIN or password.
- Something you have e.g. – mobile device, token, proximity access card, or digital certificate.
- Something you are – e.g. a fingerprint, hand scan, or an iris scan.
B
A backup is redundant data retained solely for the purposes of restoring operations following a disaster, configuration error or data loss.
A baseline recovery test is a process by which a system is restored in an isolated environment, brought to boot, and login tested with basic file level or other validation. For example: Locating a VM (object) in Cohesity, choosing the latest recovery point, and performing an "instant recovery". Once powered on, authenticating with username/password and performing a file level check for consistency with the production machine.
A Business Critical (Tier 2): Applications that play a significant role in supporting key business functions or processes, but their failure might have workarounds, albeit with potential delays or inefficiencies.
A Business Necessary (Tier 3): Applications that are important for the smooth running of certain business operations but have alternatives or for which downtimes are manageable without severe disruptions.
C
A cipher or “cypher” is a method or algorithm used to encrypt or encode information to maintain its confidentiality.
Controls are technical, administrative, or physical safeguards. Controls are the nexus used to manage risks through preventing, detecting, or lessening the ability of a particular threat from negatively impacting business processes. Controls directly map to standards, since control testing is designed to measure specific aspects of how standards are implemented.
Control Objectives are targets or desired conditions to be met. These are statements describing what is to be achieved as a result of the organization implementing a control, which is what a Standard is intended to address. Where applicable, Control Objectives are directly linked to an industry-recognized secure practice to align cybersecurity and privacy with accepted practices. The intent is to establish sufficient evidence of due diligence and due care to withstand scrutiny.
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI): As outlined in Title 32 CFR 2002.4(h), CUI is “information the Government creates or possesses, or that an entity creates or possesses for or on behalf of the Government, that a law, regulation, or Government-wide policy requires or permits an agency to handle using safeguarding or dissemination controls.” For more information regarding specific CUI categories and subcategories, see the DoD CUI Registry website.
Core IT Infrastructure is the collection of essential, shared technology resources that provide the platform for all other IT functions. A disruption to this foundation will have a widespread, cascading impact on other systems and, consequently, the business operations they support.
Criticality is representative importance of system or service based on objective factors: See APM:APM Worksheet: Application Criticality - Smartsheet.com
D
Dark Web is a hidden part of the Internet that is not accessible from traditional web browsers such as Google Chrome, Safari, Internet Explorer, Firefox, etc. The Dark Web is estimated to be close to 90% of the overall Internet. Many illicit activities are known to take place on this part of the Internet including drug trafficking, illegal weapons trade, prostitution, terrorism, etc.
Data refers to raw, unprocessed text, facts or figures that lack context on their own. [In this document, data and information might be used interchangeably].
Data Availability refers to methods for ensuring that required data is always accessible when needed, in accordance with university retention policies.
Data Confidentiality refers to methods for ensuring that access to sensitive data is limited to authorized individuals.
Data Custodian is university personnel or designated third-party agent responsible for the operation and management of information systems which collect, manage, process, or provide access to University Data. See University Information Asset Classification & Management Policy for roles and responsibilities of Data Custodians.
Data Flow Diagram is a visual representation that maps out the flow of information for any process or system. It uses defined symbols like rectangles, circles and arrows, plus short text labels, to show data inputs, outputs, storage points and the routes between each destination. Sample Diagram
Data Integrity refers to methods for ensuring that data is complete, accurate, consistent, and safeguarded from unauthorized modification.
A Dependency Diagram is a visual representation that maps out the relationships and dependencies between various applications, services, databases, and other components within an IT environment.
Digital Certificate ("certificate") are a file connected to a cryptographic key pair used to confirm identity, secure communications between parties, and ensure integrity of transmissions. The use of certificates is one method of encrypting sensitive (Export Controlled, High risk [red], Moderate risk [amber], etc...) data while in transit or at rest.
Digital certificates can include, but are not limited to the following:
- SSL Certificates
- Single-Domain Certificate: A SSL Certificate is a single-domain webserver certificate needed to enable SSL operation on a server. These certificates will secure a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). For example, “example.uoregon.edu” would be secured by a single-domain certificate. This certificate would not be valid for any other FQDN than example.uoregon.edu
- Multi-Domain Certificates (SAN Certificate): A SAN (Subject Alternative Name) certificate has a field that specifies alternate FQDN’s that can use the certificate on the same domain. These certificates will secure up to 100 different FQDN’s on a single certificate
- Wildcard Certificates: A “wildcard” SSL certificate is a certificate that matches any FQDN of a sub-domain. For example, “example.uoregon.edu” is a sub-domain of “uoregon.edu.” The certificate that contains “*.example.uoregon.edu” is an example of a wildcard certificate. This certificate can be used on any server whose hostname is in the “example.uoregon.edu” domain, e.g, “www.example.uc.edu,” “mail.example.uc.edu,” or “ftp.example.uoregon.edu.” Note that only one level of sub-domain is matched, so “*.example.uc.edu” does not match “www.email.example.uoregon.edu.”
- Code Signing Certificates
- A code signing certificate is used by a developer, at the time a program is compiled, to verify the integrity of the signed program. This is equivalent to shrink wrap, or a hologram seal used in the real world to assure a product is genuine.
- Client Certificates
- Client Certificates or Digital IDs are used to identify one person to another, a person to a device or gateway or one device to another device. Typically, these are used for:
- Digital Signatures
- Email Encryption
- Client Certificates or Digital IDs are used to identify one person to another, a person to a device or gateway or one device to another device. Typically, these are used for:
Self-Signed Certificates
- Self-signed certificates are public key certificates that their users issue on their own behalf, as opposed to a certificate authority (CA) issuing them.
E
An employee refers to any individual who performs work or services on behalf of the university, regardless of compensation or formal employment status. This includes but is not limited to: full-time and part-time faculty and staff, student workers, contractors, volunteers, courtesy faculty, associate affiliates, and any other individuals granted access to university IT resources or sensitive data in the course of their duties.
An encryption key is a parameter or piece of information used by a cipher to control the encryption and decryption processes. A key serves as the essential input to a cipher algorithm, determining the specific transformation applied to the plaintext during encryption and the reverse transformation during decryption.
End of life, a designation by the vendor when a product is unable to be supported and should be replaced. This generally occurs when the operating system is no longer supported, and the hardware cannot support a new operating system.
Endpoint/Endpoint device is an electronic computing device that connects to a network and communicates back and forth with that network. Endpoints include desktop computers, laptop computers, tablets, mobile devices, or any similar network enabled device.
F
Federal Contract Information (FCI): As defined in section 4.1901 of the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR), FCI is “information, not intended for public release, that is provided by or generated for the Government under a contract to develop or deliver a product or service to the Government, excluding information provided by the Government to the public (such as that on public websites) or simple transactional information, such as that necessary to process payments.”
A functional recovery test is specific to system type. As an example: An Application server and database server, both restored in an isolated environment. Connectivity is tested between both systems, and application functionality is verified.
G
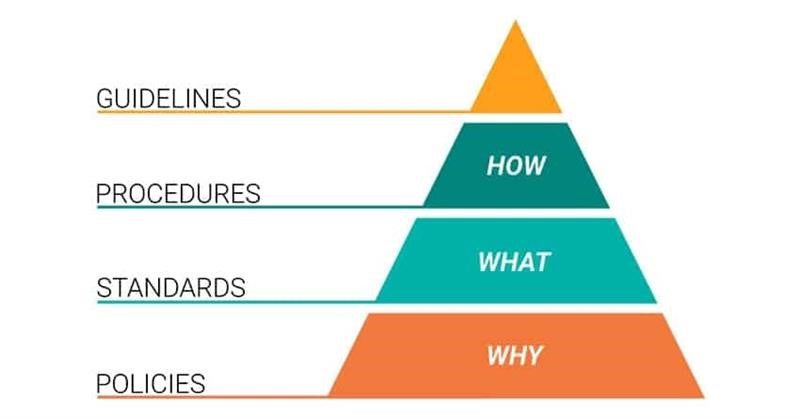
Guidelines are recommendations which can be customized and used in the creation of procedures or to help explain policies and standards.
H
I
An Incident Response Playbook is a structured, step-by-step guide that outlines how an organization should detect, respond to, and recover from various types of cybersecurity or IT incidents. It ensures consistency, speed, and effectiveness in handling incidents, especially under pressure.
Information is data that has been organized, interpreted, and given context to become meaningful and useful for decision-making; essentially, information is processed data that provides insights and understanding. [In this document, data and information might be used interchangeably].
Internet facing refers to systems, services, or devices that are directly accessible or exposed to the public Internet.
IP Address is an identifier, based on the Internet Protocol (IP) standard (RFC-791), for computer systems and devices connected to the campus network.
The ITDR program is the Information Technology Disaster Recovery program.
J
K
L
Large Language Model (LLM) refers to powerful machine learning or Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms that can generate human-like text, understand natural language, trained on massive datasets of text and are designed to predict the next word in a sequence, allowing them to perform tasks like translation, summarization, and content generation.
Local Access refers to all connections to a University resource performed directly through the system console or console serial connection.
M
MAC Address or Media Access Control address, sometimes referred to as a hardware or physical address, is a unique, 12-character alphanumeric attribute that is used to identify individual electronic devices on a network.
Mission Critical (Tier 1): Applications that are indispensable to the primary objectives or core functions of the organization. Failure or unavailability of such applications could severely disrupt operations or jeopardize the mission of the organization.
Mean time to restore (MTTR) refers to the average time it takes to restore a service following a downtime incident, focusing on the speed of recovery rather than full issue resolution.
N
Network-based Access refers to all connections to a University resource performed via a network (e.g., University wired or wireless network, remote networks).
O
P
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is defined as any data element or combination of data elements that would be sufficient to be used to fraudulently assume the identity of an individual, consistent with the Oregon Consumer Identify Theft Protection Act (OCITPA). Examples of this type data include a person’s name in combination with one or more of the following:
- Social Security number (SSN)
- Note: UOIDs or 95#s are treated as Moderate
- W2s, W4s, I9s
- Driver’s license number or state identification card number
- Identification number issued by a foreign nation
- Passport number
- Bank Account number, Credit or Debit Card number, in combination with any required security code, access code or password that would permit access to a consumer’s financial account
- Biometrics
- Date of Birth
- Personal Data of covered “data subjects” defined under the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) including:
- Name
- Government-issued IDs
- Photo
- IP address or web cookies
- Health information
- Genetics, race or ethnic origin
- Biometrics
- Sex life or sexual orientation
- Political opinions
- Religious or philosophical beliefs
- Trade/union
- Criminal convictions.
A Playbook is a very detailed document that lists (links to) all critical information for a specific system/product. Including: Service Managers and Owners, Dependencies, Recovery Team Membership and many other pieces of critical information. The use cases for a "playbook" are many, but at its core, it will be used to guide the recovery of the system/service itself.
In lieu of the ITDR supplied playbook, a department specific document/ playbook is sufficient if it's accurate, contains key information and is available.
Principle of Least Privilege (POLA) is a principle that each subject in a system be granted only the most restrictive set of privileges needed for the performance of authorized tasks. The application of this privilege limits the damage that can result from accident, error or unauthorized use.
The principle of separation of duties involves dividing roles and responsibilities among multiple individuals to ensure no single person has complete control over a process. For instance, someone responsible for creating accounts and assigning permissions should not have the ability to modify the logs that monitor these activities.
A privileged account refers to a user whose permissions are restricted to the specific systems, applications, or data necessary to perform their job responsibilities. These users typically do not carry out administrative tasks and are not classified as privileged users.
A production recovery test is when all components are restored from backup and brought online in a production environment. This includes full user testing, connectivity testing and integrity testing (including rollback).
Policy defines the security objectives and the security framework of the UO.
Procedure is a detailed step by step how-to document that specifies the exact action which will be necessary to implement important security mechanisms.
Q
R
The university has an organization wide Records Retention Schedule (RRS) that applies to data and documents. Because backups are redundant data retained solely for the purposes of restoring operations following a disaster, configuration error or for data loss purposes, they are not generally considered the official record. As a general rule, back-ups should never be kept for longer than the RRS retention period of the records represented by the back-up. Backups should be disposed of (or overwritten) as soon as immediate use ceases and as appropriate within a documented back-up cycle unless the administrator has received instructions, typically from the Office of General Counsel, to preserve a specific back-up. For more information about the Records Retention Schedule, please see recordsmanagement.uoregon.edu/rrs.
Registered device or system means either install vulnerability scanning agent or configure system with appropriate credentials to facilitate authenticated vulnerability scanning operation.
Registered and configured for ISO ongoing vulnerability scans means that the ISO can conduct vulnerability scans against the device as is necessary for compliance, security, or policy reasons.
Resource Administrator – this may variously refer to a service administrator, system administrator, database administrator, network administrator, or device/endpoint administrator depending on the resource in context. I.e., a resource administrator is the person who is responsible for, configures or administrates, a system, device, application, or service.
To restore is the process of copying systems from a backup—typically stored on a separate disk or locations—to the original location or other appropriate file locations.
S
Sensitive data is Information classified as High Risk (Red) or Moderate Risk (Amber) under the University of Oregon’s Information Asset Classification & Management Policy. This includes any data whose exposure could cause harm—such as financial loss, identity theft, or discrimination—and any data regulated by governmental entities where improper handling could result in repercussions for the university. This includes, but is not limited to:
- High Risk (Red) data: Loss or exposure could cause serious strategic, financial, compliance, or reputational harm.
- Examples: Social Security Numbers, health records (PHI), financial account details.
- Moderate Risk (Amber) data: Loss or exposure could cause moderate harm to university operations or reputation.
- Examples: Student grades, internal HR files, budget planning documents.
A server is a specialized computer or software system designed to provide services, data, or resources to other clients over a network.
A Service Account is a local, domain, or cloud-based account not typically associated with human use. It is used by automated processes, services, or applications to interact with operating systems, access databases, run scripts or batch jobs, and perform API calls. These accounts often support password automation to streamline secure access and operations. A service account may also be considered a privileged account if it holds elevated permissions beyond those of a general user or has full access within an application.
Service Provider – is a unit or person who provides Resource Administrator’s functions to a collection of information systems resources.
Standard is a mandatory action that gives formal policies support and direction.
Standard End-User refers to a user whose permissions are restricted to the specific systems, applications, or data necessary to perform their job responsibilities. These users typically do not carry out administrative tasks and are not classified as privileged users.
Supported system or application means that the entity providing the system or application, be it a vendor, open source, or an individual, is actively and routinely providing and deploying patches and security updates for the system or application.
System, Application, and Service can be loosely defined as any electronic environment that stores, processes or transmits information for the purpose of maintaining the operational functions of University.
T
A tabletop exercise is a specific simulated scenario (security, technical failure, etc.), targeted against a system or service to replicate an outage. Conducted from incident beginning to resolution. This will be facilitated and led by the ITDR Office.
Top-level Administrator or their designee is the head of the college, department, or unit (e.g., Vice Provost/Vice President/Dean/Department Head).
A Top-Level Perspective will serve as a starting place for any IT service for the university. As an example: The "Data Backup service offering" encompasses all Core Infrastructure systems used to copy, store, and defend our data from cyberattacks, human error, and natural disasters. The TLP serves as a high-level overview that provides links to information (ITDR playbooks) for each product, contact information, department home page and a service description.
TOR Network (https://www.torproject.org/about/overview.html.en) is the most common mechanism used to access "Dark Web" resources; it provides anonymity to users.
Two-factor Authentication (a.k.a., Two-Step Login, 2FA) is defined as a second layer of security to protect an account or system. Users must go through two layers of security before being granted access to an account or system. The University of Oregon provides a Two-Step Login service that uses DUO Security to manage the second factor authentication.
U
University computing and information resources are a collection of systems, applications and services that are in the custody of the University.
University of Oregon (UO) Computing Resources means university-owned, licensed or managed data stored in any form (e.g., electronic, paper, or any other medium), hardware (e.g., central processing unit, computer memory and peripherals, file storage, Internet of things devices), software, network infrastructure, Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, email accounts, and domain names, regardless of location, whether on-premises, in the cloud or elsewhere.
University of Oregon (UO) Records means any record as defined in the university records management policy IV.10.01.
An unsupported system or application means the developer or vendor is no longer issuing timely software patches or security updates.
User (of UO Computing Resources) means any individual who attempts to access or has access to UO Computing Resources.
V
Vulnerability Scanning is an automated, high-level test that looks for and reports potential known vulnerabilities.
W
A walkthrough is an all-team review of Playbooks.